What Happens To Human Body In Space? Space Exploration
- Team WOS
- 8 Mins Read
What Happens To Human Body In Space? How much difference a human being will feel while being in space? Watch this video for better understanding!
Aftermath of World War II
World war II ended and the world witnessed two new superpowers, the USA and USSR. Once allies, now they were competing with each other to have maximum influence over the world. The race to supremacy started the tactical cold war during the latter half of the 20th century. It started with the nuclear race, a race to build the most massive nuclear weapon possible.
Trinity testing started the race and Tsar Bomba won the finale. Nuclear warfare also included projectile missiles that could carry the nuclear warhead for a long distance. The quest to increase the range of those missiles gave these two countries an upper hand.
It was just a matter of time when somebody could have thought of adopting this technology and launching it as far as possible from the Earth. This led to the use of rocket technology, which can put satellites around the orbit of the planet.
Orbital mechanics was quite well known at that time and it was the engineering aspect that evolved during the post-world-war era. The USSR led the way and launched the first satellite Sputnik in 1957. During the Sputnik-2 mission they launched the first animal into space. It was a dog named Laika, sent there to be studied in the microgravity environment.
The USA was on the back foot and they launched Project Mercury in 1958 intending to launch men into the Earth’s orbit. Subsequently, the USSR too started its secret man mission known as Vostok. Human beings were about to reach space. The question one may ask is what will the conditions be for the human body in space. How much difference a human being will feel while being in space?
First's in Space
Initially, all manned missions were orbital based and men remained inside the space capsule all along but it was in 1965 when cosmonaut Alexei Leonov performed the first spacewalk there. He remained floating in outer space for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. When we are talking about humans in space, how can we forget the first man to go into space?
It was another soviet, Yuri Gagarin. Inside the space capsule Vostok 1, he completed one orbit around the earth in 1961. He was the first one to share the feeling of a person in space. He told how he was hanging in a horizontal position and suspended in the microgravity condition. These experiences tell us about the condition of the human body in space.

Yuri Gagarin before his epic spaceflight on April 12, 1961. Credit: Smithsonian Magazine
And not just human beings but a lot of animals have been sent up there to study the conditions so that we could help prepare a safe flight for a human mission. The US sent fruit flies to space in 1947 to study the effect of radiation.
Fortunately, they returned alive, and then a monkey, Albert II was sent in 1949. Apes, cats, mice all have their name as species that reached outer space. Sadly a lot of them were dead. Around 2/3rd of the monkeys sent up there died during the mission. Laika died too because her oxygen ran out and there was a case of overheating in the capsule.
Space is scary
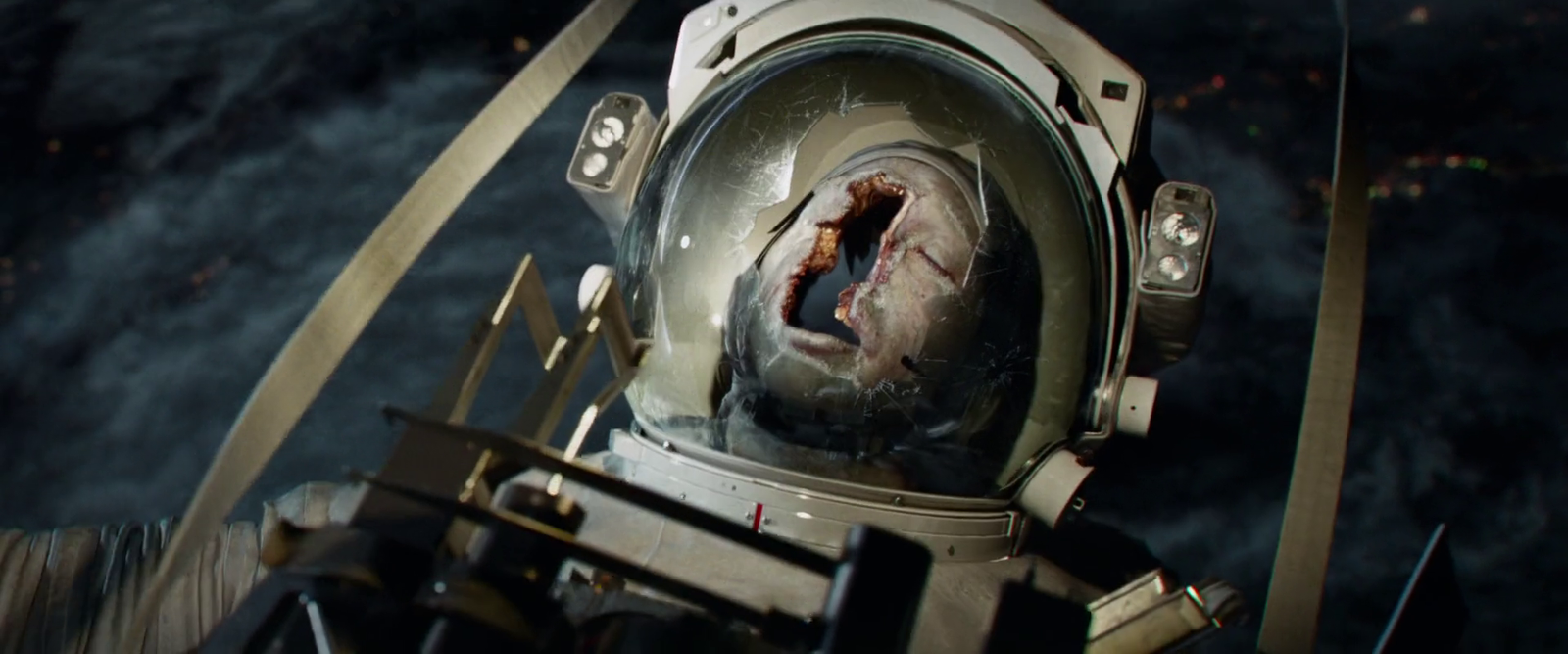
Space is scary and lonely, and conditions are nothing like that of earth. It is way too cold with an equilibrium temperature of 2.7 Kelvin, i.e. the temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background. It is inhospitable, completely vacuum (of course if we do not consider the quantum effects), and the pressure is so low that it will make human blood boil at such low temperature.
But one thing we may note here is that the main problem in space is not the temperature but the pressure. Space does not have any temperature of its own. Temperature is a function of energy in a particular amount of mass but space is not filled with any mass. Also since space is a vacuum, the thermal transfer cannot possibly happen through conduction and convection.
Only thermal radiation is predominant there. When we would be in space without a spacesuit, depending upon the exposure of our body to the sun, we would feel warm or cold. There is no one-sided explanation. Since there is no conduction and convection, our body will not lose heat instantly but the heat transfer will happen at a slightly slower rate through radiation alone. No one will instantly freeze or be boiled.
Game of Pressure
Since the pressure in outer space is so low, the pressure inside our body will be greater than that of the outside that will make our lungs expand which can cause lungs rupture or sudden death. As the pressure is reduced, the boiling point of the liquid lowers down. Thus the blood inside our vessels will start to boil even at that cold temperature and convert into water vapor. This process is called Ebullism. Our tissues will begin to swell and due to the presence of gas bubbles in the blood vessel, there will be a blockage in the bloodstream.
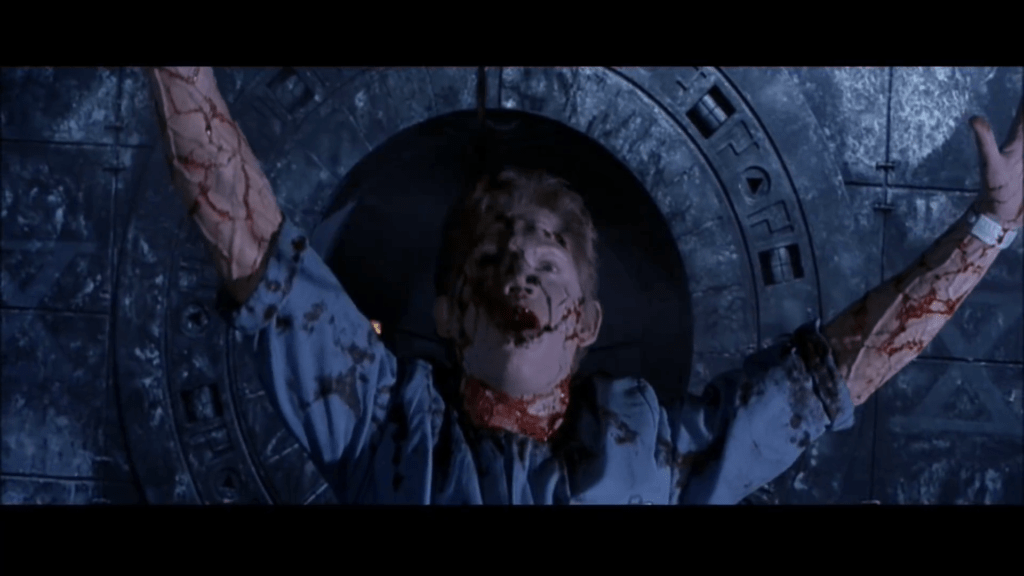

The final state of any human body without a spacesuit will be death and definitely not an easy one.
Since inside pressure is more, oxygen will diffuse out of the bloodstream and this will cause oxygen deprivation and the condition is known as hypoxia. The deoxygenated blood will reach the brain and we will become unconscious. Within minutes we will die. Thus the final state of any human body without a spacesuit will be death and definitely not an easy one.
Effects of microgravity on Human Body in space
Even when the astronauts reach space in their spacesuit, the environment is still not as favorable and there are many problems associated with it too. Microgravity affects the body very badly and physiological adaptation is not that easy. Fitness gets down; some astronauts even lose their ability to function well when they return to earth.
NASA astronaut Anne McClain is carried from the landing site after returning from more than 200 days on the space station in2019. It can take astronauts more than a week to fully regain their balance after extended stays in space. Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
Low gravity affects the blood circulation while blood does not flow down to the legs and the upper part of the body is filled with a lot that makes the face look puffy. It subsequently reduces the circumference of the leg making astronauts feel weaker down the body. Low gravity causes the body to remain afloat a lot of time and thus the muscles below the waist do not work that much. This condition leads to muscle atrophy.
Harmful ionizing radiations can even penetrate the spacesuit and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and eye defects. The amount of RBCs gets reduced, the immune system gets affected. Sometimes astronauts feel the loss of taste and smell. Even their sleep cycle is destroyed and bright flashes in the back of the eye while sleeping is common among them. Depression and anxiety are one of the main concerns for astronauts coming back home and millions of dollars are spent on these astronauts by the government for maintaining their mental health.
Space travel seems fascinating but as you have seen, it is not a Disneyland ride. By learning this, we can have some more respect for the astronauts who put their lives at risk for the cause of scientific exploration.
Have you ever dreamt of becoming an astronaut and floating in space? Let us know in the comments.
Share this article
Team WOS
We make people fall in love with science.
Share this article
Douglas AdamsSpace, it says, is big. Really big. You just won't believe how vastly, hugely, mind-bogglingly big it is.
Latest posts
We have learned many partial truths and some remain with us even when we are studying higher courses. Let’s look up such partial truths that are very common...
How do the animals and birds view the world around them? Do they perceive everything just like a human? Let's understand the basic anatomy of the eyes of...
Here is a list of the best science books that'll take you deep into the ocean of science. Books fueled the mighty revolutions in human history and produced...
World's most renowned scientists think that the cosmos has quantum consciousness. First of all, what exactly is consciousness? Scientists are actively engaged experimental tests of these ideas. One approach is to study brain-impaired patients to see if their information...
Trending Articles
Is ISRO The Best Space Agency? ISRO's incredible journey is the story of India’s jump to orbit! In 1962, APJ Abdul Kalam was selected for the job of rocket engineer at the Indian Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR)...
World's most renowned scientists think that the cosmos has quantum consciousness. First of all, what exactly is consciousness? Scientists are actively engaged experimental tests of these ideas. One approach is to study brain-impaired patients to see if their information...
How do the animals and birds view the world around them? Do they perceive everything just like a human? Let's understand the basic anatomy of the eyes of...
Climate has changed in the past on its own but modern pollution has been its severe accelerator. Let’s look at some of the huge disasters that happened in the past few years due to climate change.
Is Pluto a planet or not? The debate over its classification rages on, with some scientists advocating for a return to its original status. The controversy over Pluto's planetary status raises larger questions about how we define and categorize objects in space
Here is a list of the best science books that'll take you deep into the ocean of science. Books fueled the mighty revolutions in human history and produced...